Fishing net sizes vary depending on the target species and fishing environment. Smaller nets are ideal for catching bait or small fish, while larger nets are designed for larger species or commercial use. Selecting the right net size is crucial for efficient and sustainable fishing.
Table of Contents
Fishing Net Sizes
| Net Size | Suitable Use | Fish Species |
|---|---|---|
| Small (4-8 ft) | Catching bait, small fish, and recreational fishing | Minnows, Shrimp |
| Medium (9-14 ft) | Inshore and coastal fishing, targeting mid-sized species | Bass, Trout, Snapper |
| Large (15-25 ft) | Offshore and commercial fishing, targeting medium sized species | Tuna |
| X-Large (25+ ft) | Offshore and commercial fishing, targeting large species | Sharks |
Fishing Net Mesh Size
| Mesh Size | Target Species | Suitable Use |
|---|---|---|
| 1/8 – 1/4 inch | Minnows, small shrimp | Bait catching, aquarium use |
| 1/2 – 3/4 inch | Larger shrimp, small baitfish, juvenile fish | Bait catching, recreational fishing |
| 1 – 1 1/2 inches | Herring, sardines, perch, crappie | Inshore fishing, targeting small-medium fish |
| 2 – 3 inches | Bass, trout, snapper, mackerel, mullet | Inshore and coastal fishing |
| 4 – 6 inches | Tuna, salmon, grouper, large snapper | Offshore fishing, targeting larger species |
| 7 – 12 inches | Sharks, marlin, large tuna, billfish | Offshore and commercial fishing |
Fishing Net Sinker Size
| Sinker Size (oz) | Suitable Net Size | Target Species | Suitable Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 – 0.5 | Small | Minnows, small shrimp, small baitfish | Bait catching, aquarium use, shallow water |
| 0.75 – 1.5 | Medium | Herring, sardines, perch, crappie, bass | Inshore fishing, targeting small-medium fish |
| 2 – 3 | Large | Trout, snapper, mackerel, mullet | Inshore and coastal fishing, deeper water |
| 4 – 6 | X-Large | Tuna, salmon, grouper, large snapper | Offshore fishing, targeting larger species |
| 7 – 10 | XX-Large | Sharks, marlin, large tuna, billfish | Offshore and commercial fishing, deep water |
Types of Fishing Nets
Cast Nets
Cast nets are circular nets thrown by hand over an area where fish are present. They have weighted edges, which cause the net to sink quickly and encircle the fish. Once the net reaches the bottom, the angler pulls a rope attached to it to close it, capturing the fish. Cast nets are ideal for catching baitfish and smaller fish species in shallow waters.
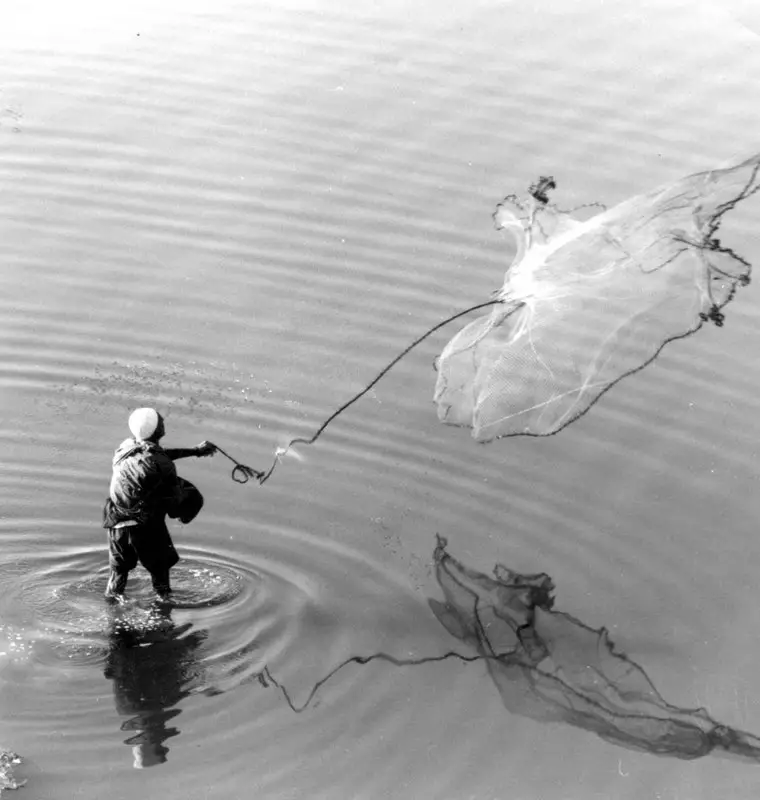

Gill Nets
Gill nets are mesh nets designed to trap fish by their gills. They are set vertically in the water, anchored or drifting, and can be used in various depths. The net’s mesh size is critical, as it determines which fish species are caught while allowing smaller fish to swim through. Gill nets are suitable for targeting a wide range of species but must be used responsibly to avoid overfishing and bycatch.

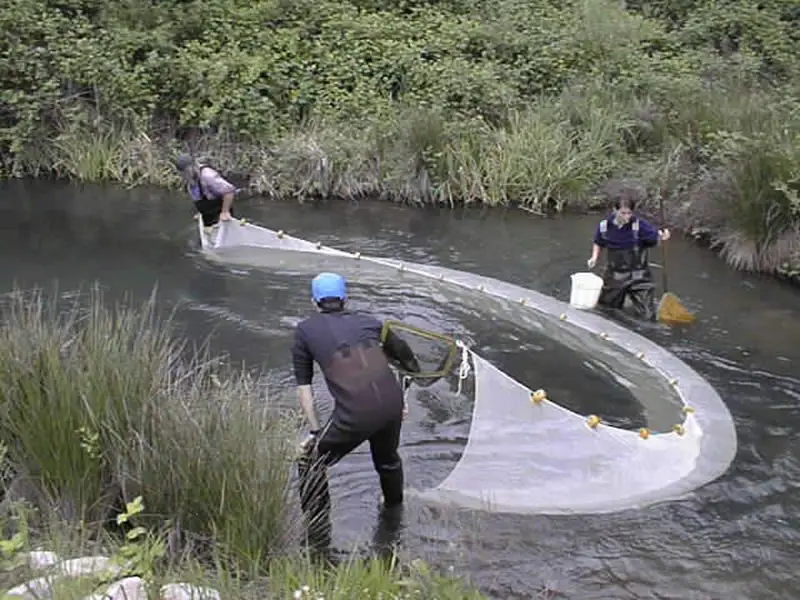
Seine Nets
Seine nets are large, vertical nets with floats on the top edge and weights on the bottom edge. They are used to encircle a school of fish, trapping them within the net. There are two primary types of seine nets: beach seines, which are used in shallow waters near the shore, and purse seines, which are used in deeper waters. Seine nets are suitable for catching a wide variety of large and small fish species.

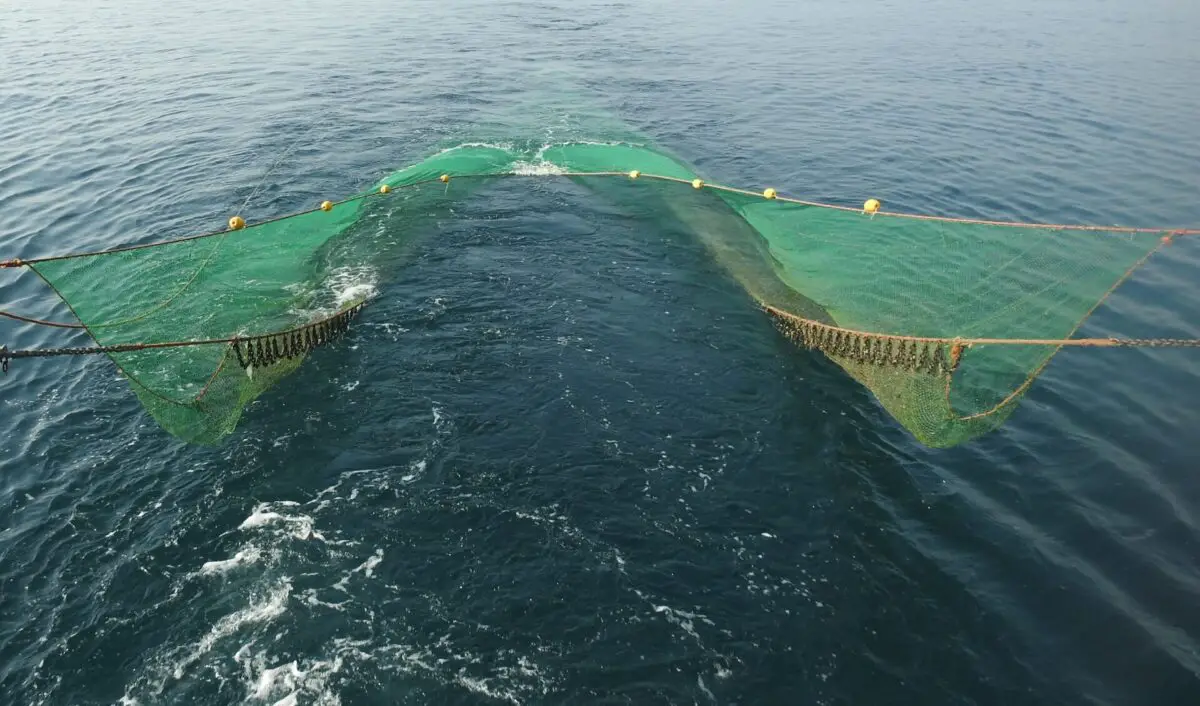
Trawl Nets
Trawl nets are cone-shaped nets towed behind a boat to capture fish. They can be used at various depths and are often weighted and held open by otter boards. Trawl nets are designed to target specific fish species or sizes, depending on the mesh size and trawling depth. However, trawl nets can result in a significant bycatch if not used responsibly.

Drift Nets
Drift nets are free-floating nets set horizontally in the water column to target fish in open water. They are usually set at night when fish are more likely to be near the surface. Drift nets are commonly used for targeting migratory species like tuna and salmon. It is essential to use drift nets responsibly to prevent ghost fishing, which occurs when lost or abandoned nets continue to catch and kill marine life.

Fyke Nets
Fyke nets are long, cylindrical nets held open by a series of hoops. They have funnel-shaped entrances that allow fish to enter but make it difficult for them to escape. Fyke nets are often used in shallow waters, such as estuaries and coastal areas, to target eel, catfish, and other species that live near the bottom.
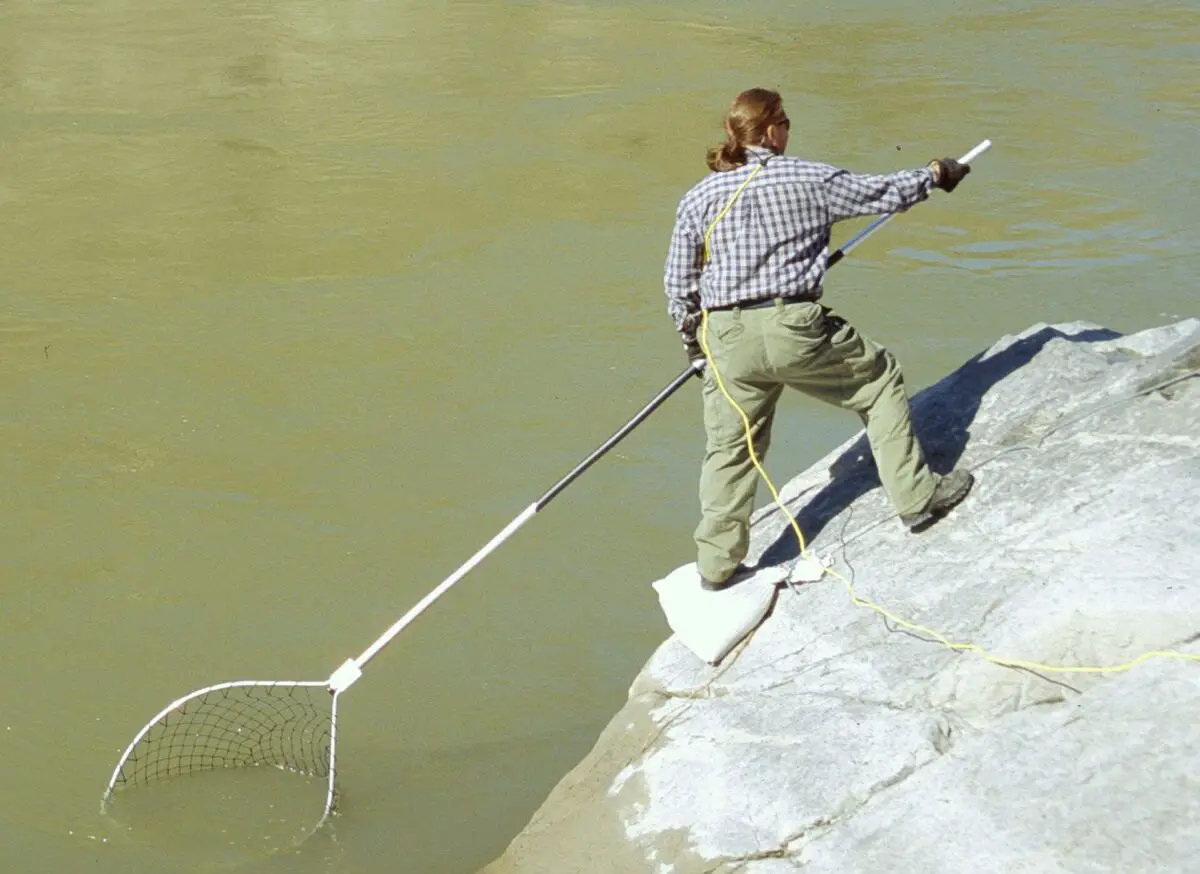
Dip Nets
Dip nets are small, handheld nets with a long handle, used for scooping fish out of the water. They are often used to land larger fish caught on a hook and line or catch smaller fish in shallow waters. Dip nets are popular among recreational anglers and can target a wide variety of fish species.

Components of a Fishing Net
A fishing net is composed of several essential components that work together to capture fish effectively. These components include:
Netting Material
The netting material is the most crucial part of a fishing net. It is typically made from synthetic fibers such as nylon, polyester, or polyethylene. The material’s strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion are vital factors. The netting can also be treated with UV protection and anti-fouling agents to prolong lifespan.
Mesh Size
The mesh size refers to the size of the openings in the net. It is essential in determining which fish species the net can capture. Smaller mesh sizes are suitable for catching small fish or bait, while larger mesh sizes target larger fish species. Selecting the right mesh size is crucial to ensure sustainable fishing practices and minimize bycatch.
Floats
Floats are attached to the top edge of the net to keep it suspended in the water. They can be made from various materials, including foam, cork, or plastic. Floats help maintain the net’s shape, make it more visible, and ensure it stays at the desired depth.
Sinkers
Sinkers, or weights, are attached to the bottom edge of the net to help it sink and maintain its position in the water column. They can be made from lead, steel, or rubber-coated weights. The size and weight of the sinkers will depend on the net size, target species, and fishing environment.
Ropes
Ropes are integral to a fishing net, connecting various components and allowing the angler to control the net. They are usually made from synthetic materials like polypropylene, nylon, or polyester, which offer strength, durability, and resistance to the elements. Ropes can secure the net, close it around the fish, or retrieve it from the water.
Brailles
Brailles are a series of lines or ropes that connect the lead line (bottom edge) to the handline (top edge) in cast nets. They enable the angler to close the net, trapping the fish inside. Brailles are usually made from the same material as the other ropes in the net.
Frames or Hoops
In some fishing net types, like fyke nets, frames or hoops are used to maintain the net’s shape and hold it open. These structures can be made from metal, plastic, or wood.
