The main parts of a fishing rod are the rod tip, guides, rod blank, reel seat, handle or grip, butt, ferrules (for multi-piece rods), hook keeper, and foregrip. Each part plays a role in casting, line control, hook setting, and fish fighting, contributing to the overall fishing performance.
| Part | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Rod Tip | The end of the rod. Used to detect fish bites and for casting. |
| Guides | Rings attached along the length of the rod to direct the line and reduce friction during casting and retrieval. |
| Rod Blank | The main body of the rod, typically made of fiberglass, graphite, or composite material. Provides the power and action of the rod. |
| Reel Seat | The part of the rod where the reel is attached. |
| Handle/Grip | The part of the rod held by the angler. Made from various materials for comfort and grip, such as cork, EVA foam, or synthetic materials. |
| Butt | The end of the rod handle. Used for leverage when casting and fighting fish. |
| Ferrules | Connect multiple pieces of a rod together (for multi-piece rods). |
| Hook Keeper | A small loop or ring for attaching the hook when the rod is not in use. |
| Foregrip | The part of the handle located above the reel seat. It gives extra grip when casting or reeling in a fish. |
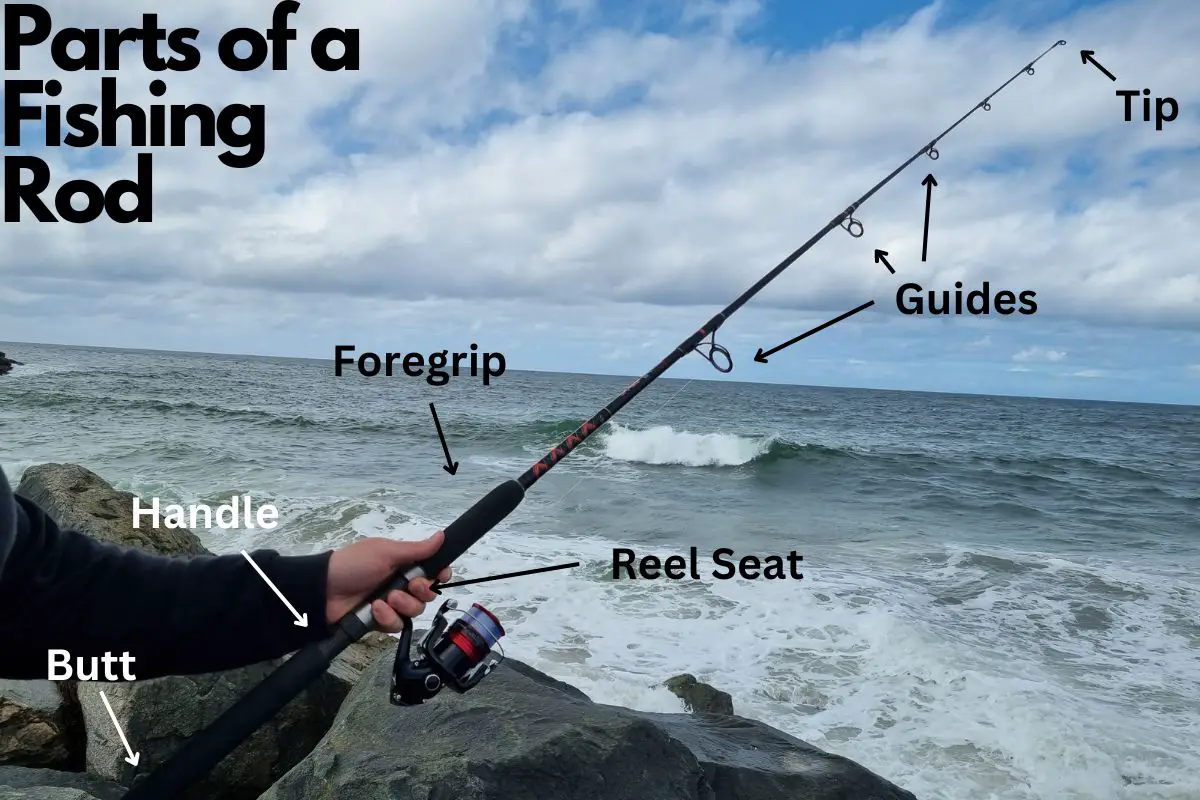
Table of Contents
Rod Tip
The rod tip, made from the same material as the rod blank, is usually the thinnest and most sensitive part. High-quality rod tips can relay information about what’s happening at the end of the line to the angler’s hand, making them crucial for detecting subtle bites. Solid tip technology integrates the tip and the blank into a single piece for enhanced sensitivity and strength. Protecting the rod tip is crucial as it’s susceptible to breaking, especially when mishandled or stored improperly.
The most likely way to destroy a fishing rod is when the rod tip is slammed into the bed of your truck during transport. I always pay particular attention to my rod tips and cover them in a towel for extra protection during transportation.
Guides
Guides are circular or oval rings that help manage the fishing line along the rod. They are typically made of durable, low-friction materials such as ceramic, titanium, or stainless steel. Fuji guides, a notable technology in the market, offer high-quality guide rings that resist grooving, thereby increasing casting efficiency and line longevity. Regular inspection for damage and cleaning to remove grit can prevent line wear and ensure smooth casting and retrieval.
Quick Tip: Never store your hook by clipping it on to one of the guides and tensioning the line by cranking the handle. Over time this can damage the guides which will start rubbing on your line and cause a break at the worst possible time.
Rod Blank
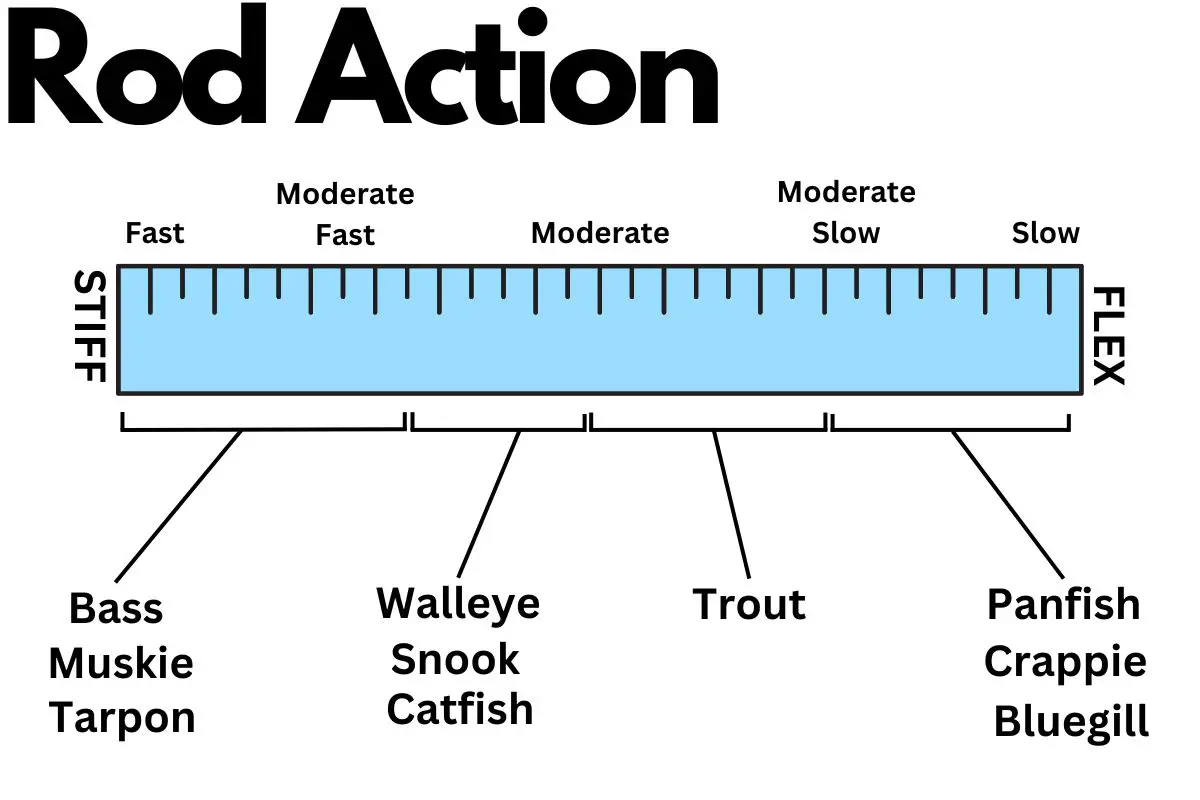
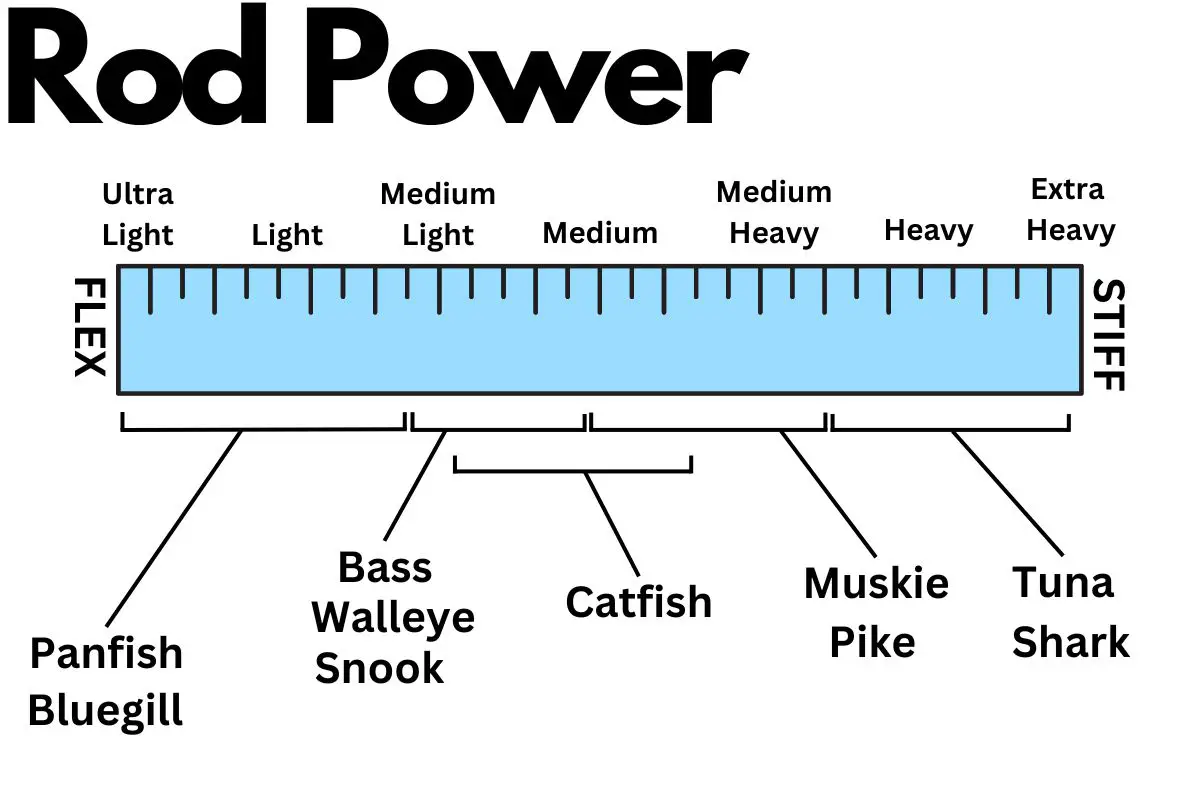
The rod blank, which makes up the core of the fishing rod, largely determines the rod’s action (flexibility) and power (resistance to bending). Modern technologies include graphite for high sensitivity and lightness, fiberglass for rugged durability and more moderate actions, and composites for a balanced blend of characteristics. Taking care not to strike or crush the rod blank can avoid hidden damage that may cause it to fail during a crucial moment.
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Lightweight, very sensitive, stiff (fast action) | Brittle, less durable, more expensive | High-performance fishing, such as competitive angling |
| Fiberglass | Durable, flexible (slow action), cheaper | Heavier, less sensitive | Techniques where durability and flexibility are essential, such as trolling |
| Composite (Graphite/Fiberglass Blend) | Balances sensitivity and durability, moderate action | Heavier than pure graphite rods, not as sensitive as pure graphite or as durable as fiberglass | Techniques where durability and flexibility are essential, such as trolling or crankbait fishing |
| Carbon Fiber | Very light, highly sensitive, strong | Expensive, less durable than fiberglass | High-performance fishing such as competitive angling |
Reel Seat
The reel seat anchors the fishing reel to the rod. Durable materials like graphite or anodized aluminum can resist corrosion and securely hold the reel. Some models use cushioned hoods over the reel foot for a snug fit, minimizing reel movement during use. Ensuring the reel seat remains sturdy and free from corrosion prevents reel instability or even the complete loss of a reel.
Handle/Grip
Handles come in various materials like cork, EVA foam, and newer synthetic materials, each offering different comfort and grip levels. Split grip, full grip, or pistol grip are some common types. A well-cared-for handle provides a comfortable and secure hold, crucial for casting accuracy and fighting fish.
My personal preference is AAA-grade premium cork. I find this gives the best non-slip grip and is also aesthetically stunning.
Butt
The butt is the end of the rod. Larger rods often have a fighting butt for additional control and leverage when fighting large fish. The butt can be simple or padded for comfort. Ensuring the butt is in good condition can improve the angler’s control, particularly when casting or reeling large fish.
Ferrules
Ferrules are the connectors on multi-piece rods. They come in various designs, with technologies that ensure a snug fit and seamless power transition, such as the spigot and sleeve-over ferrules. Ensuring the ferrules are clean and well-fitted can prevent potential rod breakage.
Hook Keeper
The hook keeper is a small loop or clip that provides a secure spot to place the hook when the rod is not in use. Keeping the hook keeper intact prevents line tangling and accidental hooking of objects (or people), making transportation and storage safer and more convenient.
If you don’t have a hook keeper, you must find somewhere else to store your hooks – don’t clip them onto your guides.
Foregrip
The foregrip, found on many casting and spinning rods, provides additional grip and control, particularly during casting or when fighting a fish. Some rods feature ergonomic designs or advanced materials for enhanced comfort and grip. Regularly cleaning and checking of the foregrip ensure it provides effective grip and control.
